
by Terry Heick
Just how can you tell if a trainee truly understands something?
They discover beforehand to play the game– inform the educator and/or the examination what they ‘would like to know,’ and even the very best assessment leaves something on the table. (In truth, a big section of the moment trainees simply don’t understand what they don’t understand.)
The concept of understanding is, obviously, at the heart of all learning, and resolving it as a problem is one of the three pillars of official learning settings and education.
1 What do they need to recognize (requirements)?
2 What (and how) do they presently recognize (assessment)?
3 Just how can they finest concerned comprehend what they currently do not (planning learning experiences and direction)?
Yet how do we understand if they understand it? And what is ‘it’?
Understanding As’ It’
Externally, there is problem with words ‘it.’ Seems vague. Frustrating. Uncertain. However everyone in some way understands what it is.
‘It’ is basically what is to be learned, and it can be a terrifying thing to both teachers and trainees. ‘It’ is everything, explained with intimidating terms like purpose, target, proficiency, test, test, grade, fall short, and be successful.
And in regards to content, ‘it’ could be almost anything: a truth, an exploration, a habit, ability, or general principle, from mathematical concept to a clinical procedure, the value of a historic figure to a writer’s objective in a text.
So if a pupil gets it, past pure academic efficiency what might they have the ability to do? There are several existing taxonomies and attributes, from Bloom’s to Recognizing by Design’s 6 Elements of Understanding
The adhering to activities are established as a direct taxonomy, from the majority of standard to one of the most intricate. The very best part about it is its simpleness: Most of these actions can be executed simply in the class in minutes, and do not need intricate planning or an extensive examination period.
By utilizing a fast layout, principle map, t-chart, conversation, image, or short action in a journal, fast face-to-face collaboration, on a departure slip, or via digital/social media, understanding can be examined in mins, assisting to replace testing and consternation with an environment of evaluation. It can be even be shown on a course internet site or hung in the classroom to aid guide self-directed discovering, with trainees checking themselves for understanding.
Exactly How This Recognizing Taxonomy Works
I’ll compose even more concerning this quickly and put this into a more visuals type soon; both of these are vital in using it. (Update: I’m also developing a program for teachers to aid the, use it.) For now, I’ll state that it can be used to direct planning, assessment, curriculum design, and self-directed understanding. Or to develop vital thinking inquiries for any content area
The ‘Heick’ finding out taxonomy is suggested to be simple, arranged as (mainly) separated tasks that vary in complexity from much less to extra. That claimed, pupils need not show the ‘highest’ degrees of understanding– that misreads. Any kind of capability to finish these jobs is a demo of understanding. The majority of tasks the trainee can complete the much better, however all ‘boxes examined’ are proof that the pupil ‘gets it.’
36 Thinking Techniques To Aid Students Duke It Out Intricacy
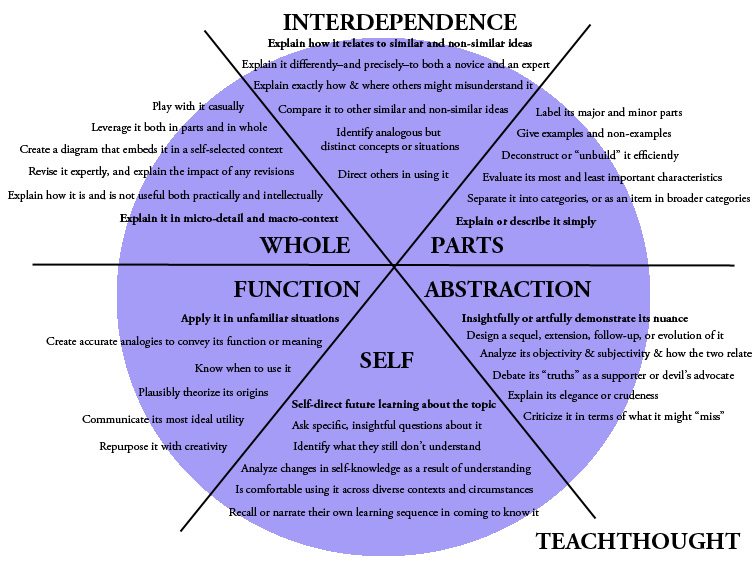
The Heick Discovering Taxonomy
Domain name 1: The Components
- Clarify or explain it just
- Tag its significant and small parts
- Evaluate its most and least crucial qualities
- Deconstruct or ‘unbuild’ it effectively
- Offer examples and non-examples
- Separate it right into classifications, or as an item in wider groups
Instance Topic
The Revolutionary War
Test Prompts
Describe the Revolutionary War in straightforward terms (e.g., an inescapable disobedience that developed a brand-new country).
Recognize the major and minor ‘components’ of the Revolutionary War (e.g., economics and publicity, soldiers and tariffs).
Assess the War of independence and identify its least and most important features (e.g., domino effect vs city names and minor skirmishes)
See additionally 20 Kinds of Questions For Showing Vital Believing
Domain 2: The Whole
- Describe it in micro-detail and macro-context
- Develop a layout that embeds it in a self-selected context
- Describe exactly how it is and is not useful both practically and intellectually
- Play with it casually
- Leverage it both in parts and in entire
- Change it skillfully, and clarify the effect of any kind of modifications
Domain 3: The Interdependence
- Explain just how it associates with comparable and non-similar concepts
- Direct others being used it
- Clarify it differently– and precisely– to both a novice and a specialist
- Clarify specifically just how and where others could misconstrue it
- Contrast it to various other comparable and non-similar ideas
- Recognize comparable yet distinct concepts, ideas, or circumstances
Domain name 4: The Function
- Use it in unknown circumstances
- Create accurate examples to convey its function or significance
- Evaluate the wonderful area of its energy
- Repurpose it with imagination
- Know when to use it
- Plausibly theorize its origins
Domain 5: The Abstraction
- Insightfully or artfully demonstrate its nuance
- Criticize it in regards to what it may ‘miss’ or where it’s ‘deceitful’ or insufficient
- Argument its ‘realities’ as a supporter or devil’s advocate
- Discuss its beauty or unfamiliarity
- Examine its objectivity and subjectivity, and exactly how both connect
- Layout a sequel, extension, follow-up, or evolution of it
Domain name 6: The Self
- Self-direct future finding out about the topic
- Ask certain, informative inquiries about it
- Recall or narrate their very own knowing sequence or chronology (metacognition) in familiarizing it
- Is comfortable using it across diverse contexts and situations
- Recognize what they still do not understand regarding it
- Assess modifications in self-knowledge as a result of comprehending
Advanced Comprehending
Recognizing by Design’s 6 facets of Comprehending, Blossom’s Taxonomy, and Marzano’s New Taxonomy were additionally referenced in the creation of this taxonomy; a learning taxonomy for comprehending